Virtual Reality Glasses: A Journey Through the History of Digital Immersion
The history of virtual reality (VR) glasses is fascinating and marks a remarkable advance at the intersection of technology and human experience. The concept of creating simulated environments for entertainment or training dates back several decades, but the modern VR glasses we know today have roots stretching back to the end of the 19th century
The great-great-grandfather of virtual reality glasses
Os efeitos visuais de alteração da realidade já eram possíveis com a utilização da fotografia estereoscópica por meio da percepção de parallax. A estereoscopia é um método que utiliza duas imagens ligeiramente diferentes para criar a ilusão de profundidade quando vistas por um observador. Esse efeito é conhecido como estereoscopia binocular, e a diferença de perspectiva entre as duas imagens é o que proporciona a sensação de parallax.
Principle of Stereoscopic Photography:
Image capture: Photographers took two pictures of the same scene, usually positioning the camera at a slightly horizontally displaced point, simulating the distance between human eyes.
Stereoscopic visualization: These two images were then mounted or displayed side by side on a specific device, such as a stereoscope. The stereoscope was an optical device that allowed each eye to see only one of the images, thus creating a three-dimensional perception of the scene.
Parallax effect: When looking at the two images with each eye, the human brain combined the visual information, generating the sensation of depth and parallax. Nearby objects appeared displaced in relation to more distant objects, replicating the natural effect that human eyes experience when viewing the real world.
The technique of stereoscopic photography played an important role in introducing the idea of three-dimensionality into visual perception, influencing the later development of technologies such as 3D cinema and, eventually, virtual reality.
The Beginning of the Journey
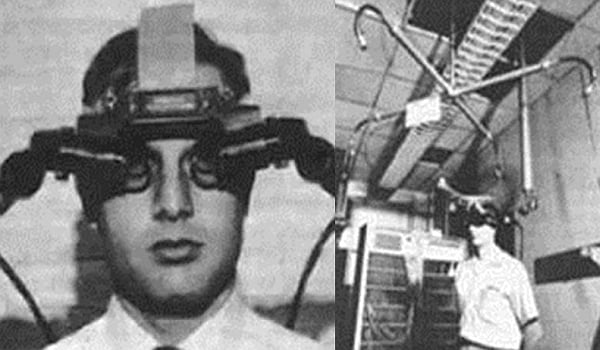
The first steps in the creation of virtual reality devices as we know them were taken in the 60s and 70s. Ivan Sutherland and his team developed "The Sword of Damocles" in 1968.
The "Sword of Damocles" was a metal structure suspended over the user's head, creating a sense of three-dimensional involvement. The device's main function was to display rudimentary graphics, providing a unique visual experience for users. However, there were significant challenges associated with the device, especially in relation to its considerable size and weight.
Despite technological advances, its dissemination to the general public was impractical due to its very characteristics. The excessive size and weight made the device uncomfortable and limited its accessibility. This initial period of virtual reality was characterized by enthusiastic experimentation, but the technical limitations of the time imposed barriers to the widespread adoption of this revolutionary technology.
The 80s and 90s: An Era of Experimentation
In the 1980s and 1990s, virtual reality technology experienced a period of popularization, although it still faced substantial challenges in terms of quality and accessibility. During this time, renowned companies in the entertainment sector, such as Sega and Nintendo, launched peripherals that sought to offer users immersive experiences.
These peripherals, often associated with video game consoles, promised to transport players to immersive virtual environments. However, the technological limitations of the time resulted in experiences of limited quality. Images were often pixelated, response to movement could be slow, and immersion was compromised by technical glitches. Even so, these early efforts were crucial in popularizing the idea of virtual reality among the general public.
In addition to technological advances, the 1980s and 1990s also saw the emergence of the term "virtual reality". Jaron Lanier, one of the notable pioneers in the field of virtual reality, coined this expression to describe digital experiences that transported users into simulated environments. Lanier played a significant role in publicizing and promoting virtual reality, helping to establish the terminology that is now commonly used.

The Resurgence of the 2000s
In the 2000s, virtual reality glasses underwent a remarkable renaissance, driven by significant advances in hardware and software. One of the pioneering companies in this period was Oculus VR, founded by Palmer Luckey in 2012. The launch of the Oculus Rift in 2016 marked a turning point in the history of virtual reality.
Oculus VR's virtual reality glasses represent a substantial evolution compared to previous attempts. One of the main improvements has been the significant reduction in the weight of the devices, making them more comfortable for users. In addition, there have been notable advances in image quality, providing a sharper and more realistic visual experience.
One of the revolutionary elements introduced by the Oculus Rift devices was motion tracking. This allowed the glasses to detect and respond to the user's head and eye movements, providing a more authentic sense of immersion. Motion tracking was a crucial step towards creating a more fluid and interactive virtual reality experience.
The success and positive acceptance of the Oculus Rift catalyzed renewed interest in virtual reality, not only in the gaming industry, but also in various applications such as training, simulations and educational experiences. Other companies, realizing the potential of the market, began to invest in and develop their own virtual reality devices, contributing to an exponential increase in the variety and quality of these products.
Current Expansion
The growing interest in virtual reality has triggered a veritable technological race, with several major companies entering the scene to explore and improve this exciting technology. Prominent names such as HTC, Sony and Microsoft have become active participants in this field, each bringing their unique vision to the world of virtual reality.
The HTC ViveThe HTC Vive, launched by HTC, stood out as one of the most advanced devices on the virtual reality market. Equipped with motion sensors, precise tracking and a wide playing area, the HTC Vive offered a remarkable immersive experience, especially for gaming enthusiasts and technology enthusiasts.
Sony also entered the scene with the PlayStation VRIt was designed to be compatible with the PlayStation console. This opened up a new front for virtual reality, integrating it directly into Sony's existing gaming ecosystem and providing an accessible experience for many console users.
Microsoft, for its part, introduced Windows Mixed RealityThis has helped to diversify the market, offering an open platform for various manufacturers to develop their own virtual reality devices. This approach has contributed to the diversification of the market, providing a variety of options for consumers to choose from.
In addition to these advances, the constant improvement of smartphones has also played a crucial role in popularizing virtual reality. Many mobile devices are now able to support virtual reality experiences via specific adapters and glasses. This has brought VR to a wider audience, allowing people to experience this exciting technology without the need for dedicated devices.
A significant milestone in this respect was the emergence of autonomous devices such as the Oculus Quest, a creation of Oculus VR (acquired by Facebook). The Oculus Quest eliminated the need to connect to a computer or console, providing a completely autonomous and accessible experience. This kind of innovation has further democratized access to virtual reality, allowing more people to enjoy immersive experiences without complex barriers.
Applications Beyond Games
A tecnologia de realidade virtual rapidamente transcendeu suas origens e expandiu-se para diversas áreas, tornando-se uma ferramenta versátil e inovadora em muitos setores.
In medicine, virtual reality has been widely adopted to improve the training of healthcare professionals, especially surgeons. Virtual surgical simulations offer a safe and controlled environment for practicing complex procedures, allowing surgeons to hone their skills without risk to real patients. These simulations also make it possible to practice specific surgeries and become familiar with advanced techniques, contributing to better performance in the real operating room environment.
In industry, virtual reality is used to optimize the design process and employee training. Companies can create virtual environments to design products, allowing detailed three-dimensional visualization even before physical production. In addition, VR is employed in employee training, offering interactive simulations that replicate real-world situations. This is particularly valuable in sectors such as manufacturing, construction and complex operations, where virtual practice can increase efficiency and safety.
In education, virtual reality is transforming the way students learn. Virtual environments provide immersive educational experiences, allowing students to explore concepts in interactive and engaging ways. For example, history lessons can transport students to important historical moments, while science lessons can allow virtual exploration of cells or ecosystems. This more hands-on and immersive approach has the potential to significantly improve understanding and retention of content.
In addition to these areas, virtual reality has been adopted in fields such as therapy, architecture, armed forces training, virtual tourism and much more. The expansion of virtual reality into these diverse sectors highlights its versatility and the positive impact it can have on various areas of society.
Challenges and future prospects
Despite the advances, virtual reality still faces challenges. Issues related to physical discomfort, the need for powerful hardware in most cases and the price still limit its mass adoption. However, the constant evolution of technology, including the development of new interfaces and sensors, suggests that virtual reality will continue to improve.
The history of virtual reality glasses is a journey of innovation and overcoming challenges. From the early days of computer graphics to today's autonomous and interactive devices, VR has transformed from a futuristic idea into a constantly evolving technological reality. As technology advances, we can expect virtual reality experiences that are increasingly immersive, impactful and integrated into our daily lives.